Callable statement consist of three parameters we used the form with a result parameter, which means that we must set it as an OUT parameter.
To clarify I have numbered the parameters:
Authors is Stored procedure name it takes three parameters.i clearly explain below.
{call authors(?,?,?)}
1 2 3
In out
CREATE PROCEDURE authors (p_auth_id varchar(15), OUT p_auth_fname varchar(20), OUT p_auth_lname varchar(20))
Above example takes the first one in IN parameter, the second and third are OUT parameters and returns a result.
Therefore the correct way to call it is:
Create a CallableStatement object to call the store procedure.
CallableStatement stat1 = con.prepareCall(“{call authors(?,?,?)}”);
CallableStatement stat1 = con.prepareCall("{call authors(?,?,?)}");
stat1.setString(1, "1");
stat1.registerOutParameter(2,Types.VARCHAR);
stat1.registerOutParameter(3,Types.VARCHAR);
Parameter 1 is an IN-only parameter the stored procedure doesn’t return any other value besides the OUT-parameters.
To read the result from the OUT-parameters we also have to adapt the parameter numbers:
System.out.println(stat1.getString(2));
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println(stat1.getString(3));
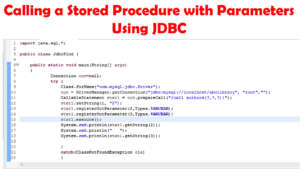
i have attach the full Code below.
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcFind {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection con=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/abclibrary", "root","");
CallableStatement stat1 = con.prepareCall("{call authors(?,?,?)}");
stat1.setString(1, "2");
stat1.registerOutParameter(2,Types.VARCHAR);
stat1.registerOutParameter(3,Types.VARCHAR);
stat1.execute();
System.out.println(stat1.getString(2));
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println(stat1.getString(3));
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException cle)
{
System.out.println("check your jdbc connection" );
}
catch(SQLException sqe)
{
System.out.println("Check connection" +sqe);
}
finally
{
try{
if(con != null)
con.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
I have attached the video tutorial below it will help you to do this step by step.