This tutorial will teach you to make a small shop Grocery Shop Inventory management system in java.how make a system.in in java step by step. The following system will use to manage the Grocery Shop sales calculation. If you are an interested in pos in java this is the right place where you will able learn inventory management system java more projects. 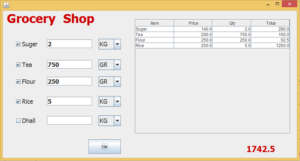
Features of the System
- User shall be able to select the item what they need.
- User shall be able to calculate the total
Paste the code inside the ok button
double sum = 0;
double price;
double qty;
double cal = 0;
if(chk1.isSelected())
{
String suger = chk1.getText();
String mes= txtsum.getSelectedItem().toString();
price = 140.0;
qty = Integer.parseInt(txtsqty.getText().toString());
if(mes.equals("KG"))
{
cal = (qty * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
suger,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
else
{
cal = (qty/1000 * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
suger,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
if(chk2.isSelected())
{
String tea = chk2.getText();
String mes1= txtstut.getSelectedItem().toString();
price = 200.0;
qty = Integer.parseInt(txttqty.getText().toString());
if(mes1.equals("KG"))
{
cal = (qty * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
tea,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
else
{
cal = (qty/1000 * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
tea,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
}
if(chk3.isSelected())
{
String flour = chk3.getText();
String mes2= txtflum.getSelectedItem().toString();
price = 250.0;
qty = Integer.parseInt(txtfqty.getText().toString());
if(mes2.equals("KG"))
{
cal = (qty * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
flour,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
else
{
cal = (qty/1000 * price) ;
txtbill.setText(String.valueOf(cal));
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
flour,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
}
if(chk4.isSelected())
{
String rice = chk4.getText();
String mes3= txtricm.getSelectedItem().toString();
price = 250.0;
qty = Integer.parseInt(txtrqty.getText().toString());
if(mes3.equals("KG"))
{
cal = (qty * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
rice,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
else
{
cal = (qty/1000 * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
rice,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
}
if(chk5.isSelected())
{
String dhall = chk5.getText();
String mes4= txtdham.getSelectedItem().toString();
price = 350.0;
qty = Integer.parseInt(txtdqty.getText().toString());
if(mes4.equals("KG"))
{
cal = (qty * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
dhall,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
else
{
cal = (qty/1000 * price) ;
model = (DefaultTableModel)jTable1.getModel();
model.addRow(new Object[]
{
dhall,
price,
qty,
cal
});
}
}
for(double i=0; i <jTable1.getRowCount(); i++)
{
sum = sum + Double.parseDouble(jTable1.getValueAt((int) i, 3).toString());
}
txtbill.setText(Double.toString(sum));
}