This tutorial will teach you how to make a house rest system step by step. This system helpful you to learn JDBC connective and learn crud operation.
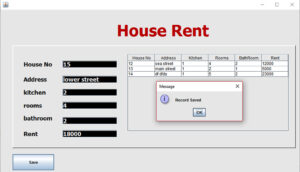
First Establish the Database Connection
Add the Sql Namespace
import java.sql.*;
Database Connection
Connection con;
PreparedStatement pst;
public void Connect()
{
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/houserent","root","");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(HouseRent.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(HouseRent.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
Paste following code inside the Save Button
String hno,address,kit,bath,rooms,rent;
hno = txtNo.getText();
address = txtAddress.getText();
kit = txtKit.getText();
rooms = txtRooms.getText();
bath = txtBath.getText();
rent = txtRent.getText();
try {
pst = con.prepareStatement("insert into records (houseno,address,kitchen,rooms,bathroom,Rent)values(?,?,?,?,?,?)");
pst.setString(1,hno);
pst.setString(2,address);
pst.setString(3,kit);
pst.setString(4,rooms);
pst.setString(5,bath);
pst.setString(6,rent);
pst.executeUpdate();
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "Record Saved");
txtNo.setText("");
txtAddress.setText("");
txtKit.setText("");
txtRooms.setText("");
txtBath.setText("");
txtRent.setText("");
txtNo.requestFocus();
Table();
}
catch (SQLException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
Load the Table
public void Table()
{
try {
pst = con.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM records");
ResultSet Rs = pst.executeQuery();
DefaultTableModel model = (DefaultTableModel) jTable1.getModel();
ResultSetMetaData RSMD = Rs.getMetaData();
int CC = RSMD.getColumnCount();
DefaultTableModel DFT = (DefaultTableModel) jTable1.getModel();
DFT.setRowCount(0);
while(Rs.next())
{
Vector v2 = new Vector();
for (int ii = 1; ii <= CC; ii++) {
v2.add(Rs.getString("houseno"));
v2.add(Rs.getString("address"));
v2.add(Rs.getString("kitchen"));
v2.add(Rs.getString("rooms"));
v2.add(Rs.getString("bathroom"));
v2.add(Rs.getString("Rent"));
}
DFT.addRow(v2);
}
jTable1.setModel(model);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
i have attached the video link below. which will do this tutorials step by step.